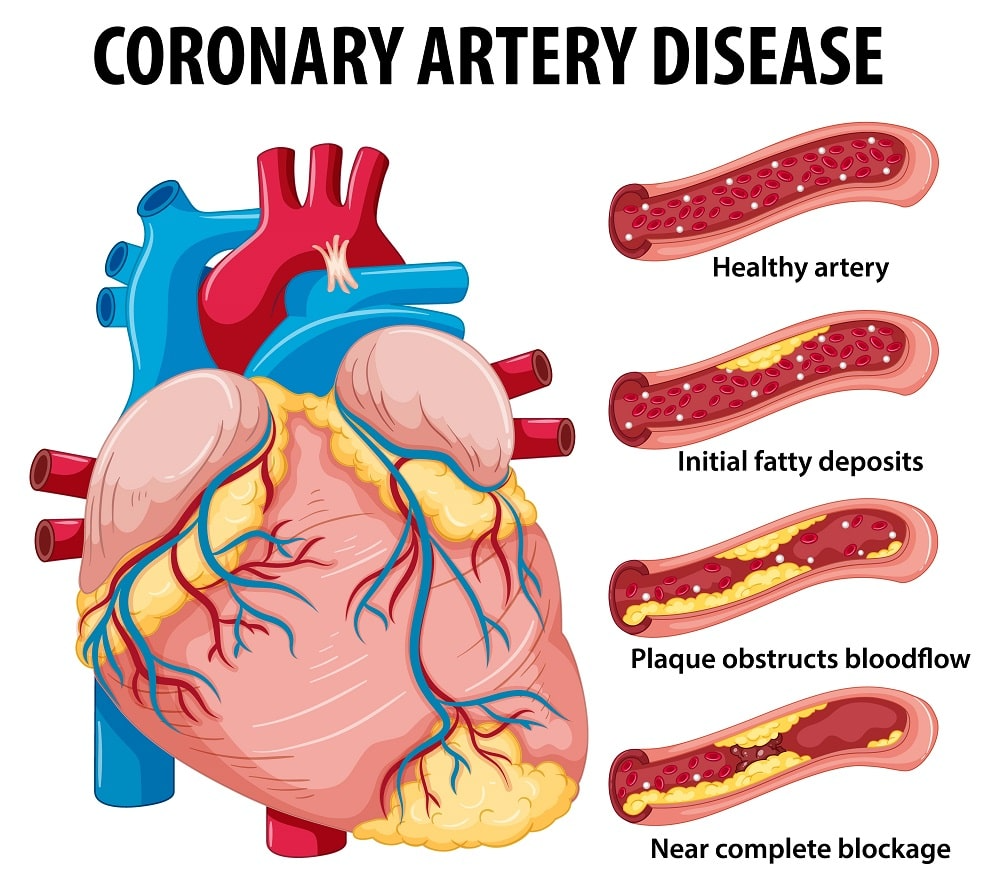
Risk Factors for Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) is the leading cause of heart attacks and a major contributor to global mortality. Understanding its risk factors is essential for prevention and early intervention.
Key risk factors include:
High Blood Pressure (Hypertension): Elevated pressure strains the arteries, accelerating plaque buildup.
High Cholesterol: Excess LDL (“bad” cholesterol) contributes to narrowing and hardening of coronary arteries.
Smoking: Tobacco damages blood vessels and promotes clot formation.
Diabetes: High blood sugar damages arteries and increases CAD risk.
Obesity: Excess weight is linked to high blood pressure, diabetes, and unhealthy cholesterol levels.
Physical Inactivity: Lack of exercise contributes to several CAD risk factors.
Unhealthy Diet: Diets high in saturated fats, trans fats, and processed foods increase risk.
Family History: Genetics can predispose individuals to early CAD.
Age and Gender: Risk increases with age; men are generally at higher risk earlier, though women’s risk rises post-menopause.
Stress and Poor Sleep: Chronic stress and inadequate sleep negatively impact heart health.
Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Can raise blood pressure and triglyceride levels.
Addressing these factors through lifestyle changes, medical management, and regular check-ups can significantly reduce your risk of CAD and improve heart health.